Understanding Chapter 7 Bankruptcy and Its Impact on Student Loans: A Comprehensive Guide
Guide or Summary:Chapter 7 BankruptcyStudent LoansChapter 7 Bankruptcy and Student LoansEligibility for Chapter 7 BankruptcyImpact on Credit ScoreAlternativ……
Guide or Summary:
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- Student Loans
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy and Student Loans
- Eligibility for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- Impact on Credit Score
- Alternatives to Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is a legal process that allows individuals to eliminate most of their unsecured debts, providing a fresh financial start. This type of bankruptcy is often considered by those who are overwhelmed by debt and unable to manage their financial obligations. Under Chapter 7, a debtor's non-exempt assets may be liquidated to pay creditors, but many individuals find that they can keep essential property through state exemptions.
Student Loans
Student loans are a significant financial burden for many individuals, especially recent graduates. These loans are designed to help students cover the costs of their education, but they can lead to substantial debt that is difficult to manage. Unlike most unsecured debts, student loans are often not dischargeable in bankruptcy, which means that individuals may still be responsible for repaying them even after filing for bankruptcy.
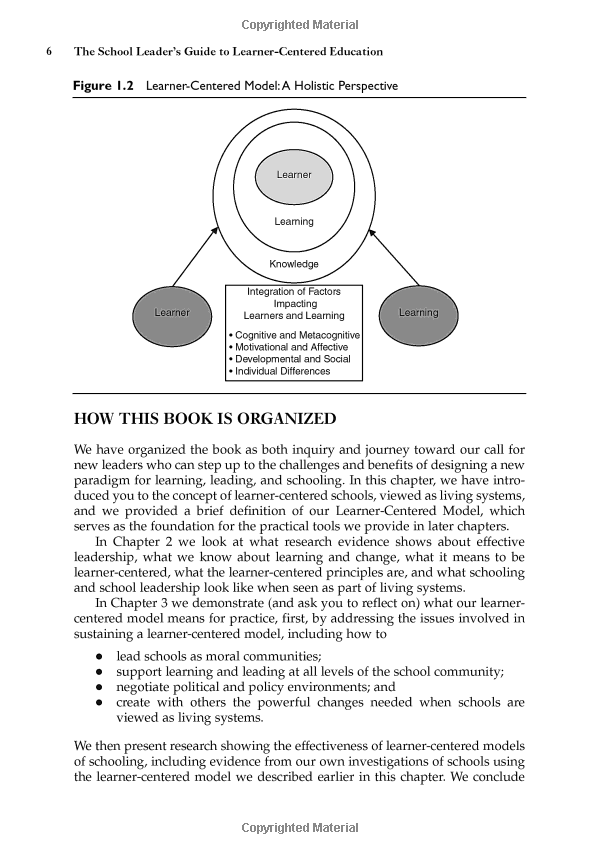
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy and Student Loans
The intersection of Chapter 7 bankruptcy and student loans is a complex issue. While Chapter 7 can provide relief from various types of debt, student loans are generally treated differently under bankruptcy law. To discharge student loans through bankruptcy, a borrower must prove that repaying the loans would cause "undue hardship," a standard that can be difficult to meet. This typically involves demonstrating that the borrower cannot maintain a minimal standard of living if forced to repay the loans, that the financial situation is likely to persist, and that the borrower has made a good faith effort to repay the loans.
Eligibility for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
To qualify for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, individuals must pass a means test, which assesses their income, expenses, and overall financial situation. If a debtor's income is below the median income for their state, they may qualify for Chapter 7. If not, they may be required to file for Chapter 13 bankruptcy, which involves a repayment plan over three to five years.
Impact on Credit Score
Filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy has a significant impact on an individual's credit score. It can remain on a credit report for up to 10 years, making it challenging to obtain new credit or loans in the future. However, for those overwhelmed by debt, the benefits of filing for Chapter 7 may outweigh the negative impact on credit.
Alternatives to Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
For individuals struggling with student loans, there are alternatives to consider before filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy. Options such as income-driven repayment plans, loan consolidation, and loan forgiveness programs may provide relief without the need to declare bankruptcy. Additionally, some borrowers may qualify for deferment or forbearance, temporarily suspending their loan payments during financial hardship.
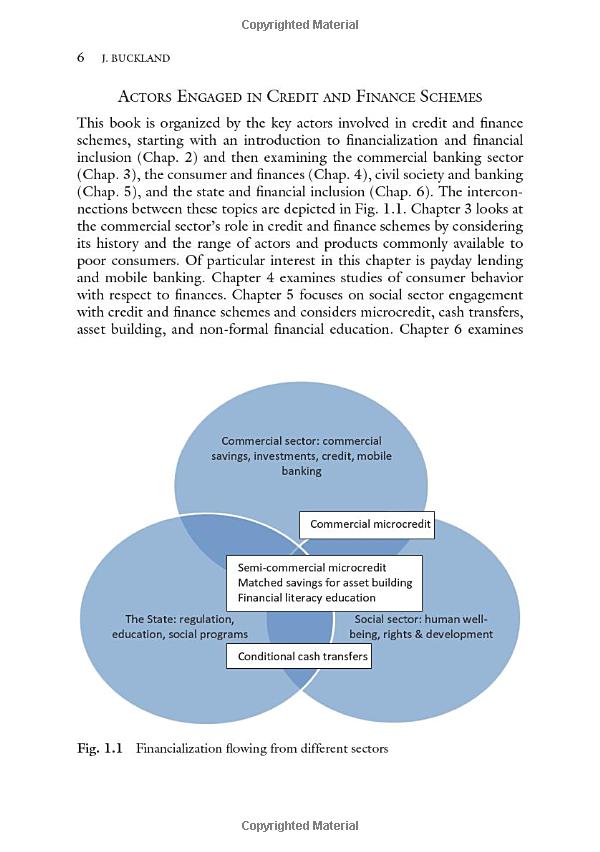
In summary, while Chapter 7 bankruptcy can provide significant relief from various types of debt, it does not offer an easy solution for student loans. Understanding the complexities of bankruptcy law and exploring all available options is crucial for individuals facing financial difficulties. Consulting with a qualified bankruptcy attorney can help navigate the process and determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances.
